Polar and Transverse Moment of Inertia
It is one aspect. 4 rows Polar Moment of Inertia is measure of an objects ability to resist torsion under specified axis.
Cylindrical Shaft Moment Of Inertia Equations
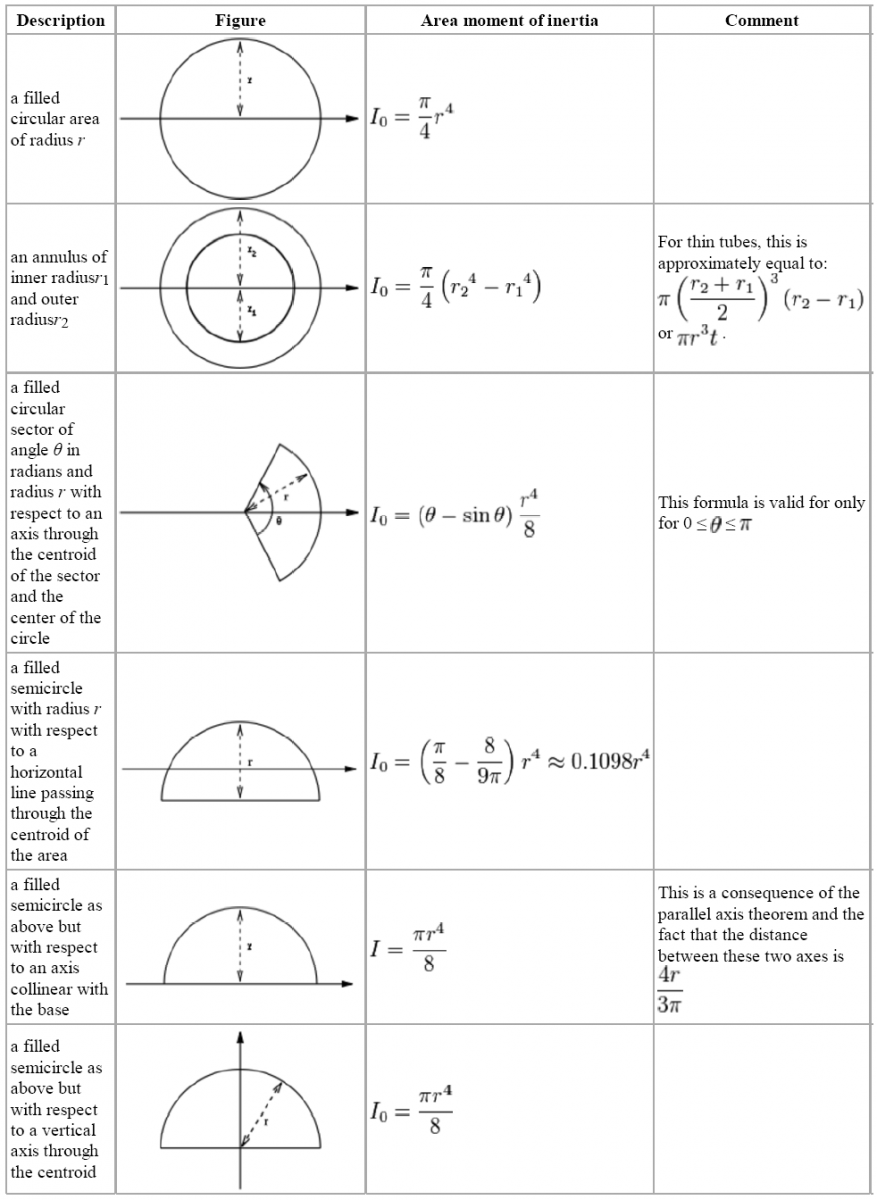
The equation of the polar moment of inertia is J r²dA.

. Full text not available from this. Moments of inertia - polar and transverse. The polar moment of inertia or polar second moment of area is a measure of an objects ability to resist torsion as a function of its shape.
Someone told me that I need an add-in. TJ τr GθL. I 2 m 0 2 m 2 R 2 4 m R 2.
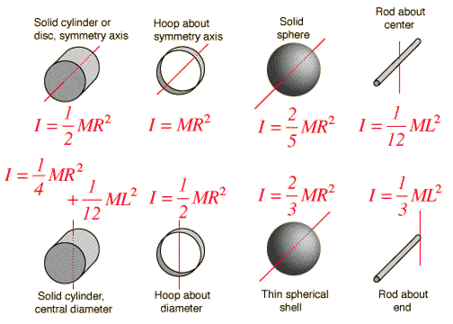
The moment of inertia otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia angular mass second moment of mass or most accurately rotational inertia of a rigid body is a quantity that. BARTLETT R GRATTON C and ROLF C eds Encyclopedia of International Sports Studies. This law to a rotating object reveals that every object has a corresponding rotational inertia that relates an applied torque to a resulting angular acceleration ie τ Jα Jω.
Polar moment of inertia is required to calculate the twist of the shaft when the. It is used in the torsion equation of shaft. 5 The polar moment of inertia has an SI unit of m⁴.
The moment of inertia MI of a plane area about an axis normal to the plane is equal to the sum of the moments of inertia about any two mutually perpendicular axes lying in the plane and. I 2 m02 m2R2 4mR2. This can result in a rotor system where the ratio of the polar and transverse moments of inertia Ip and It respectively is approaching one.
The second polar moment of area also known as polar moment of inertia or even moment of inertia is a quantity used to describe resistance to torsional deformation in cylindrical objects. By definition Polar Moment of Inertia is a measure of resistibility of a shaft against the twisting. The relation between the moment of inertia and the polar moment of inertia can be given by using the perpendicular axis theorem.
The polar moment of inertia is represented by J. As J increase in the above equation the torque produced in shaft is. The polar moment of inertia may be found by taking the sum of the moments of inertia about two perpendicular axes lying in the plane of the cross-section and passing through this point.
The SI unit for the mass. The polar moment of inertia describes the distribution of the area of a body with respect to a point in the plane of the body. The polar moment of inertia can be calculated by adding the moment of inertia about two mutually perpendicular axes that lies into the plane of the cross-section and concurrent at the.
The equation for the mass moment of inertia is 𝙸 r²dm. Alternately the point can be considered to be where a. In the case with the axis at the end of the barbellpassing through one of the massesthe moment of inertia is.
Id like to know how to get the polar moment of inertia and transverse moment of inertia using this software. J𝗈 𝙸 𝗑 𝙸 𝗒 Where J𝗈 Polar moment of inertia 𝙸 𝗑 and 𝙸 𝗒 Moment of inertia about mutually perpendicular axes x and y axis. In this paper Ip is defined as polar mass moment.

Polar Moment Of Inertia Fe Exam Ncees Reference Handbook Hollow Rod Album On Imgur Polar Moment Of Inertia In This Moment Inertia
Moment Of Inertia Calculation Formula The Constructor
Difference Between Moment Of Inertia And Polar Moment Of Inertia
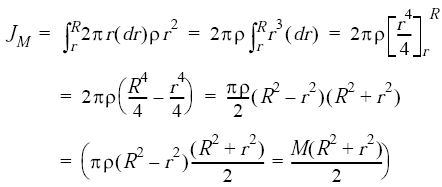
Polar Mass Moment Of Inertia About Axis A A And B B Of Common Shapes
No comments for "Polar and Transverse Moment of Inertia"
Post a Comment